Page 150 - Costellazioni 6
P. 150
GÜNTER RADDEN, Meaningful Grammar
(11c) Disposition modality
Ability, Capability: I can speak five languages.
Deontic modality is concerned with the speaker’s directive attitude to-
wards an action to be carried out. Deontic modality thus belongs to the
world of social interaction and authority. Like epistemic modality, de-
ontic modality covers the intermediate ground between the poles of re-
quest and prohibition, or Do it! and Don’t do it! Like these imperatives,
expressions of deontic modality have the force of a directive speech act.
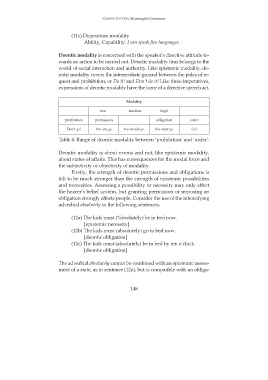
Modality
low median high
prohibition permission obligation order
Don’t go! You can go. You should go. You must go. Go!
Table 4: Range of deontic modality between ‘prohibition’ and ‘order’.
Deontic modality is about events and not, like epistemic modality,
about states of affairs. This has consequences for the modal force and
the subjectivity or objectivity of modality.
Firstly, the strength of deontic permissions and obligations is
felt to be much stronger than the strength of epistemic possibilities
and necessities. Assessing a possibility or necessity may only affect
the hearer’s belief system, but granting permission or imposing an
obligation strongly affects people. Consider the use of the intensifying
adverbial absolutely in the following sentences.
(12a) The kids must (*absolutely) be in bed now.
[epistemic necessity]
(12b) The kids must (absolutely) go to bed now.
[deontic obligation]
(12c) The kids must (absolutely) be in bed by ten o’clock.
[deontic obligation]
The adverbial absolutely cannot be combined with an epistemic assess-
ment of a state, as in sentence (12a), but is compatible with an obliga-
148